The ideal diode or perfect diode is a two terminal device, which completely allows the electric current without any loss under forward bias and completely blocks the electric current with infinite loss under reverse bias.
Ideal diodes actually do not exist. However, the V-I characteristics of ideal diodes is used to study the diode circuits. In other words, it is used to study the quality of a real diode by comparing it with the ideal diode.
It is actually not possible to design a real diode, which behaves exactly like an ideal diode. However, a well-designed diode behaves almost like a perfect diode or ideal diode.
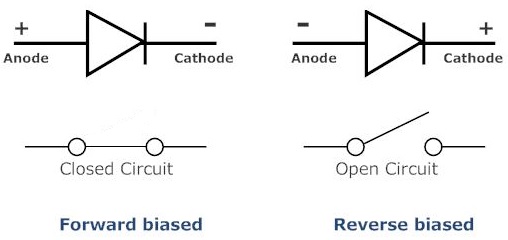
Ideal diode consists of two terminals: positive terminal and negative terminal. The positive end or positive terminal of the diode is called anode and the negative end or negative terminal of the diode is called cathode. The electric current always flow from anode or positive terminal to the cathode or negative terminal.
If the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the p-type semiconductor and the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the n-type semiconductor, the diode is said to be forward biased.
On the other hand, if the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the n-type semiconductor and the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the p-type semiconductor, the diode is said to be reverse biased.
The symbol of forward biased and reverse biased ideal diode is shown in the below figure.
Under forward biased condition, ideal diode acts as a perfect conductor with zero resistance whereas under reverse biased condition, it acts as a perfect insulator with infinite resistance. In other words, ideal diodes acts as closed circuit or short circuit under forward biased condition and acts as an open circuit or open switch under reverse biased condition.
Ideal diodes does not have depletion region or junction barrier, which resist the flow of electric current. Hence, ideal diode has no voltage drop or voltage loss.
If the forward voltage or positive voltage (VF) (p terminal connected to p-side and n terminal connected to n-side) applied on the diode is equal to zero or greater than zero, the forward electric current (IF) in the ideal diode increases infinitely.
Ideal diodes actually do not exist. However, the V-I characteristics of ideal diodes is used to study the diode circuits. In other words, it is used to study the quality of a real diode by comparing it with the ideal diode.
It is actually not possible to design a real diode, which behaves exactly like an ideal diode. However, a well-designed diode behaves almost like a perfect diode or ideal diode.
Ideal Diode symbol
Ideal diode consists of two terminals: positive terminal and negative terminal. The positive end or positive terminal of the diode is called anode and the negative end or negative terminal of the diode is called cathode. The electric current always flow from anode or positive terminal to the cathode or negative terminal.
On the other hand, if the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the n-type semiconductor and the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the p-type semiconductor, the diode is said to be reverse biased.
The symbol of forward biased and reverse biased ideal diode is shown in the below figure.
Ideal diodes does not have depletion region or junction barrier, which resist the flow of electric current. Hence, ideal diode has no voltage drop or voltage loss.
Forward and reverse characteristics of ideal diode
The Forward and reverse characteristics of ideal diode under forward and reverse biased condition is shown in the below figure.

Post a Comment